What are the different grades of tool steel?
There are hundreds of different grades of tool steel available, all with their own properties which make them more suitable to their purpose. At Wonkee Donkee, we decided to pick out some of the most conventional grades of tool steel and provide a brief description of their properties. We hope our tool steel grade guide is useful to you!
0-1 Tool Steel

An oil-hardening tool steel. Can be easily hardened at relatively low temperatures with little size change. 0-1 allows for good initial production runs, and good continued production after grinding due to its deep hardening properties and fine grain structure.
Composition (with traces of phosporus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each. Iron 96.29% minimum, carbon 0.90%, manganese 1.25%, chromium 0.50%, silicon 0.50% and tungsten 0.50%.
L-6 Tool Steel

A tough, high-strength tool steel suitable for general purpose applications. A typical application is in the making of quality hand tools and machine parts. It can be hardened to RC 63.
Composition (with traces of phosporus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each). Iron (Fe) 96.14% minimum, carbon (C) 0.70%, manganese (Mn) 0.60%, silicon (Si) 0.25%, chromium (Cr) 0.75% and nickel (Ni) 1.50%.
A-2 Tool Steel

An air-hardening medium alloy tool steel. It is heat-treatable to HRC 60-62. Easily machined prior to hardening (in the annealed condition). Negligible distortion when hardening, makes it an excellent choice for dies with complicated designs.
Composition (with traces of phosphorus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each). Iron 91.55% minimum, carbon (C) 1.0%, manganese (Mn) 1.0%, chromium (Cr) 5.0%, nickel (Ni) 0.3%, molybdenum (Mo) 1.0% and vanadium (V) 0.15 to 0.50%.
A-6 Tool Steel

This tool steel provides moderate wear resistance and toughness. It is an air hardening grade that can be hardened at a low hardening temperature.
Typical applications for A6 tool steel are blanking dies, forming dies, trim dies, stamping dies, coining dies, notching dies, bending tools, rim rolls, punches, cams, thread roll dies, spindles, retaining rings, master hobs, precision tools, mandrels, compression moulds, plastic moulds requiring high hardness, ball screws, lead screws and general purpose tooling.
Composition (with traces of phosporus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each). Iron (Fe) 95.14% minimum, carbon (C) 0.70%, manganese (Mn) 1.8 to 2.5%, silicon (Si) 0.50 maximum %, chromium (Cr) 0.90 to 1.2% and nickel (Ni) 0.90 to 1.40%.
A-8 Tool Steel

A versatile, air-hardening tool and die steel. It has excellent toughness and wear characteristics. It is ideally suited for a vast array of metal working dies and punches. Typical hardness capability; Rockwell C 55-60.
Composition (with traces of phosporus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each). Iron (Fe) 91.84% minimum, carbon (C) 0.55%, manganese (Mn) 0.5%, silicon (Si) 0.75 to 1.10%, chromium (Cr) 4.75 to 5.50%, nickel (Ni) 0.3%, tungsten (W) 1.00 to 1.50% and copper (Cu) 0.25%.
D-2 Tool Steel

A high carbon, high chromium heat treatable tool steel with excellent wear resistance. D-type tool steels contain between 10% and 18% chromium. These type of steels retain their hardness up to a temperature of 425 °C (797 °F).
Common applications for this grade of tool steel is forging dies, die-casting die blocks, and drawing dies. Due to high chromium content, certain D-grade tool steel grades are often considered stainless or semi-stainless tool steels.
Composition (with traces of phosporus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each). Iron (Fe) 82.24% minimum, carbon (C) 1.40 to 1.60%, manganese (Mn) 0.6%, silicon (Si) 0.6%, chromium (Cr) 11.00 to 13.00%, nickel (Ni) 0.3%, tungsten (W) 1.00 to 1.50%, cobalt (Co) 1.00%, molybdenum (Mo) 0.70 to 1.20% and vanadium (V) 1.10%.
S-7 Tool Steel

Shock-resistant, air hardening tool steel. High impact resistance at relatively high hardness. A tough grade which withstands chipping and breaking. Has a high attainable hardness and good wear resistance.

Note that S-2 steels have very similar properties to that of S-7 steels except that S-2 has increased vanadium content to give improved hardness and wear resistance and increased manganese content to reduce brittleness. Typical applications include chisels, dies, punches and pipe cutters.
Composition (with traces of phosporus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each).
Iron (Fe) 91.14% minimum, carbon (C) 0.55%, manganese (Mn) 0.7%, silicon (Si) 0.35%, chromium (Cr) 3.25%, nickel (Ni) 0.3%, tungsten (W) 1.00 to 1.50%, cobalt (Co) 1.00%, molybdenum (Mo) 1.40% and vanadium (V) 0.25%.
H-13 Tool Steel

The most versatile and most popular hot work tool steel. Provides a good balance of toughness, heat check resistance, and high temperature strength. It also has moderate wear resistance properties. It can be used for tool temperatures up to about 1000 F, with brief exposures up to 1100 F. Ideal for extrusion moulding dies.
Composition (with traces of phosporus (P) and sulphur (S) not exceeding 0.03% each). Iron (Fe) 91.16% minimum, carbon (C) 0.32 to 0.40%, silicon (Si) 1.00%, chromium (Cr) 5.13 to 5.25%, molybdenum (Mo) 1.33 to 1.40% and vanadium (V) 1.00%.
Cold Work Tool Steel Comparison
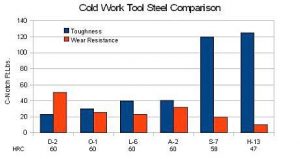
Image Credit: Simply Tool Steel.






