What are the different types of mortar joint? |
||||
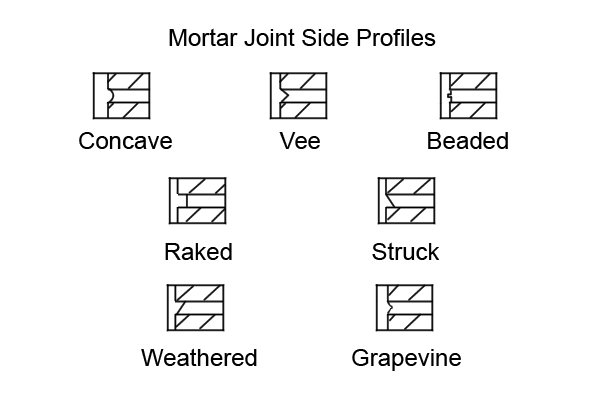
| These are the side profiles of mortar joints used in common construction. | ||||
 |
||||
 |
||||
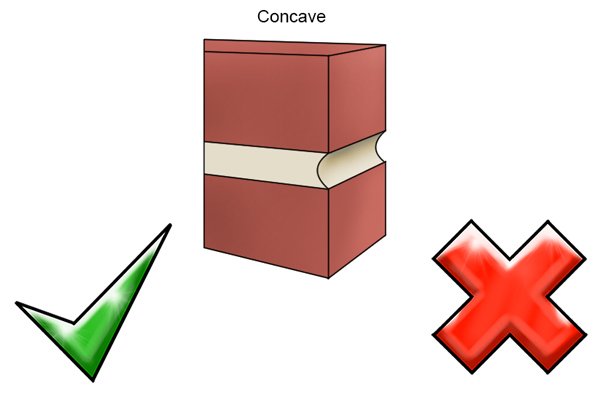
Concave joints |
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES | |||||||
 |
|
|
||||||
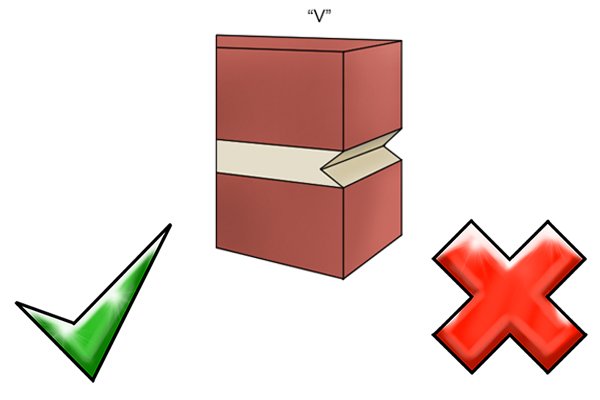
Vee or ‘V’ mortar joints |
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES | |||||||
 |
|
|
||||||
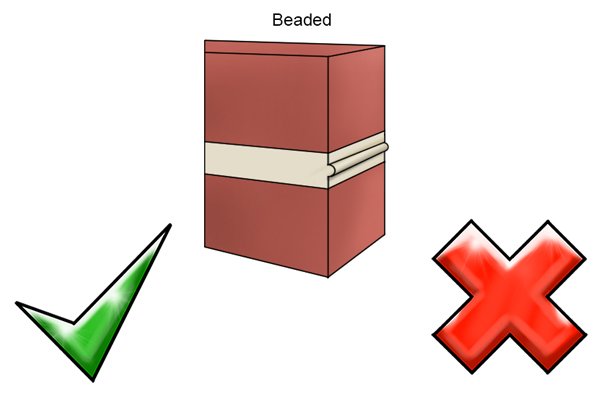
Beaded mortar joints |
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES | |||||||
 |
|
|
||||||
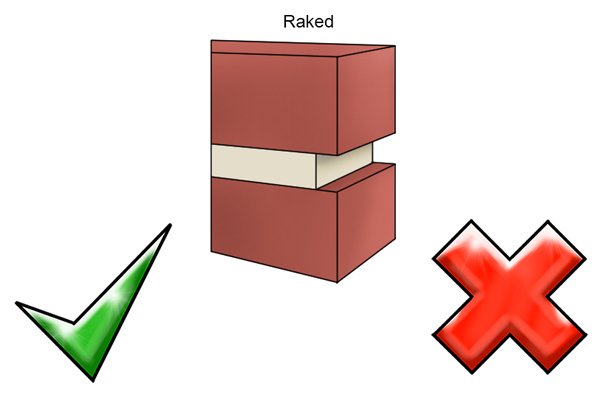
Raked mortar joints |
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES | |||||||
 |
|
|
||||||
 |
||||
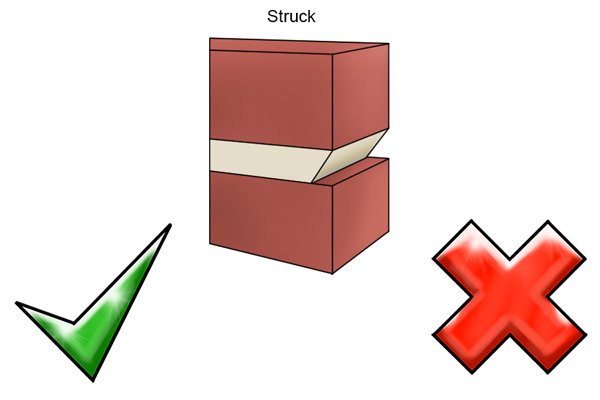
Struck mortar joints |
||||
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES | |||||||
 |
|
|
||||||
 |
||||
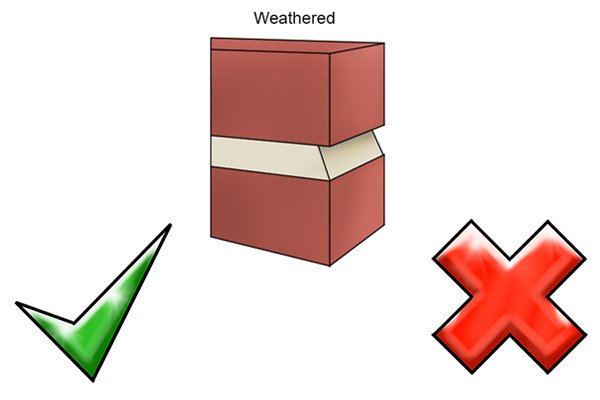
Weathered mortar joints |
||||
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES | |||||||
 |
|
|
||||||
 |
||||
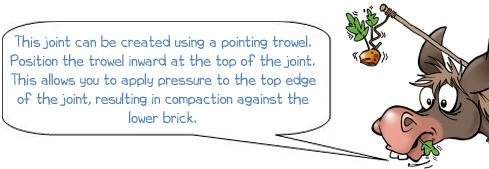
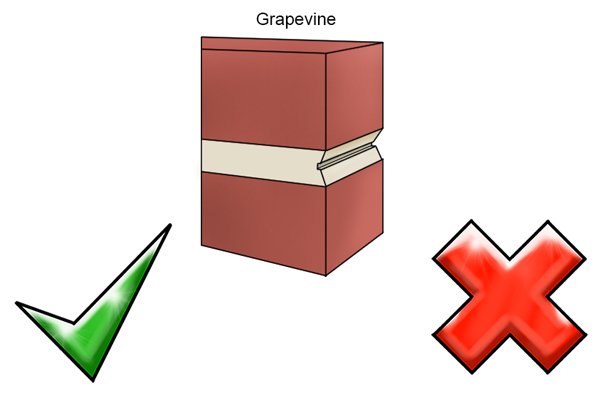
Grapevine mortar joints |
||||
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES | |||||||
 |
|
|
||||||
Additional advice when choosing a mortar joint |
||||
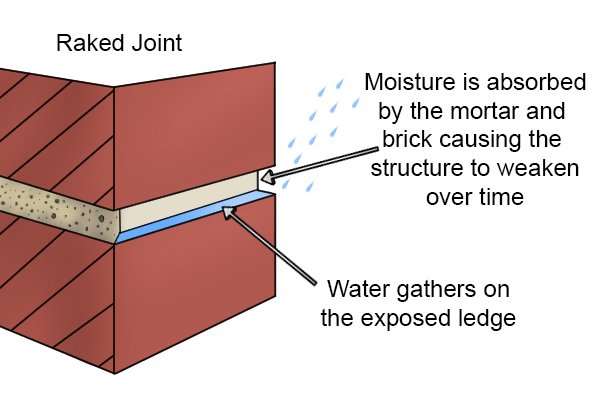 |
Avoid using mortar joints with ledges for exterior wallsYou should consider the location of the wall and its exposure to the weather when choosing an appropriate joint. Mortar joints differ in architectural appearance but also in their resistance to moisture penetration. Joints with ledges, including weathered, raked and struck joints, tend to perform poorly in exterior applications as they allow high levels of moisture penetration. Joints with ledges tend to be used for visual impact over function. |
|||
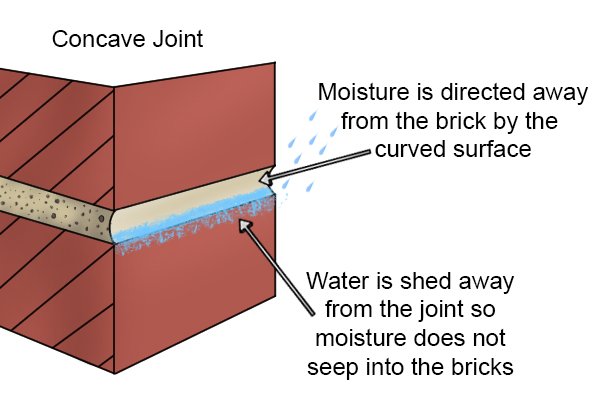 |
Choose a compact joint to improve the lifespan of bricksCompact joints, concave and vee are recommended for exterior applications as their designs create the best mortar compaction. With these joints, the bricks are less likely to need replacing as the joint is highly water-resistant. |
|||
 |
||||






